Redfish Eating Rats, Helping Gulf Coast Conservationists
John E. Phillips 02.14.14
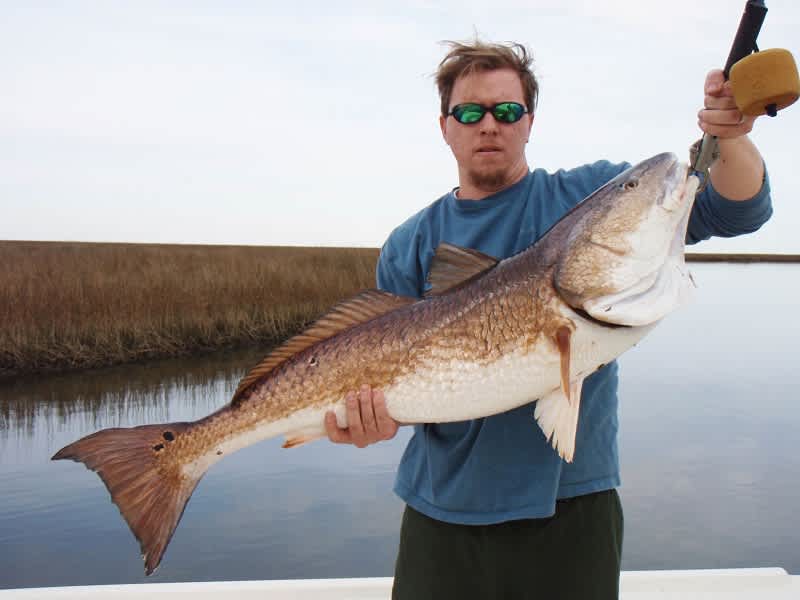

The redfish, found in abundance along the Mississippi and Louisiana coasts, is much like the catfish and will eat almost anything—dead or alive. Apparently this year, the redfish have discovered how delicious young nutria, furry creatures about one-foot long with 1-1/2-foot-long tails, are.
“As long as I have been fishing the Biloxi marsh and the waters in Louisiana and Mississippi, I’ve never seen nutria in fishes’ bellies until this fall and winter,” Darien Ladner, a guide who fishes out of Biloxi, Mississippi, and also fishes the Louisiana marshes, said.
To cross-reference this phenomenon, I contacted Captain Sonny Schindler of Shore Thing Charters in Biloxi, Mississippi. “Quite a few of our guides have noticed this same phenomenon,” Schindler explained. “Apparently, when the bull reds move inshore, they start feeding on the nutria, which burrow close to fresh and saltwater. We’ll be updating fishermen on the information we’re learning on our webpage.”

If the redfish continue to feast on young nutria, they may become the answer to controlling nutria populations all along the marshes in Mississippi and Louisiana. These 12 to 18 pound semi-aquatic rodents, originally from Argentina, destroy about 100,000 acres of wildlife-rich marshlands each year by eating the roots of the marsh grass and causing it to die. Louisiana realized it had a problem with nutria in the 1980s as fur prices declined, detrimentally impacting fur farmers who had imported the nutria.
When the price of nutria dropped below $1 each, rather than feed the animals (a nutria eats 2.5 to 3.5 pounds of food per day) that they couldn’t make a profit on, many nutria farmers opened their pens and released them. Feral populations of nutria became established in the wild, and they began to show up in the trappers’ fur harvests in the 1940s.
Nutria have webbed back feet and prefer to live in rivers, lakes, swamps, and marshes. Nutria live in burrows that often have openings at both ends with the entrances usually positioned toward a waterway above the water level. Besides their favorite foods of marsh vegetation and shellfish, nutria also will feed on crops such as cabbage, carrots, sweet potatoes, and rice. However, nutria can survive as long as a month without food. In captivity, they can live up to 12 years.
Some of the problems associated with nutria are that they can breed any month of the year, with females producing two to three litters a year of generally two to five young each. At birth, the young have fur and opened eyes and can move about and eat vegetation within a few hours. Some landowners have introduced nutria as a cure-all for ponds choked with vegetation, but once nutria get established in a lake, their high reproductive capacity soon results in overpopulation. Nutria also cause problems by damaging levees and dikes with their burrows. But nutria do have several predators, including wild cats, red wolves, large snakes, alligators, hawks, owls, eagles, and now apparently redfish.
Unlike cattle and horses that eat the tops of the plants they graze on, nutria eat the roots. They swim along canals and waterways, devouring the roots that hold the marsh grass in the mud. Then the mud and the silt once held in place by the grass falls away and becomes sludge, ruining the spawning habitat of inshore fish.
“The nutria alone don’t create the problem,” Jeff Marks, a former biologist with Louisiana’s Wildlife and Fisheries, stated. “But once they destroy the roots that hold the soil, the marsh dirt washes away during high waters or storms. The plants are what holds the marsh together; without them we have no marsh.”
Should you ever find yourself with some nutria meat on-hand, check out this delicious recipe.

Recipe for nutria sauce picante
Clean the nutria. Cover with tenderizer and Cajun seasoning overnight. Cut meat into bite-sized pieces. Use 3 to 4 pounds of meat for the following sauce recipe.
On low heat, in a large heavy pan, slowly cook seasoned meat in 1 pound of real butter (with salt) until golden brown (about 20 minutes). Add 1 cup of chopped onions, 1 cup of chopped shallots, 1 cup of diced green bell peppers, 1 cup of diced celery, 1 teaspoon of salt, 1 teaspoon of A-1 Sauce, and 1 teaspoon of white pepper. Continue to heat on low, cooking for an additional 20 minutes.
Turn heat up to medium, add 2 cans of Ro-Tel diced green chilies and tomatoes. Stir constantly for 10 minutes. Add 1 package of instant brown gravy. Turn heat to simmer. Add 2 large cans of your favorite tomato sauce. Simmer for 30 minutes. If sauce becomes thick, thin with small amounts (1/2-cup or less) of water. Adjust salt and pepper. Serve over rice or noodles.